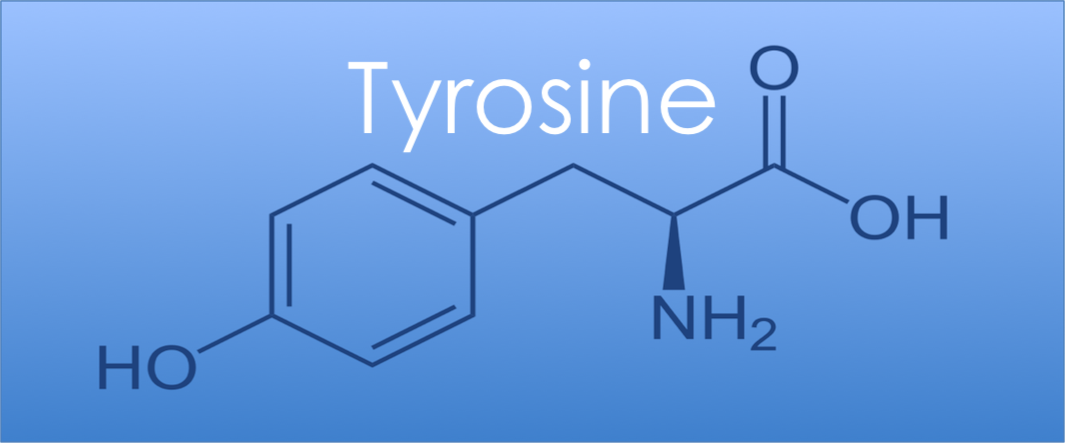
Todays post is about Tyrosine, also courtesy of Scott.
We are continuing to look at how diet and supplementation can assist with mental health.
So what is it?
Tyrosine is a nonessential amino acid that is used by the body to produce proteins. The term nonessential means that a person does not need to get it through diet, not that it is unimportant to health. It means that the body can produce it from another amino acid called phenylalanine, which is sourced through diet.
What does tyrosine do?
The body uses it to produce several important neurotransmitters. The following 3 play a vital role in many important functions.
* Dopamine: sometimes thought of as the motivational neurotransmitter, is regarded as being in charge of the 3 M’s, mood, memory and movement. It also helps support feelings of pleasure, reward, and motivation. On top of that it is also a big player in addiction, so it needs to be well balanced. Fortunately the body is very good at doing this. The absence of dopamine may contribute to attention issues, sexual dysfunction and depression.
* Epinephrine: Also known as adrenaline, this chemical plays a critical role in the fight-or-flight response.
* Norepinephrine: Also known as noradrenaline, the body releases this chemical along with epinephrine to increase heart rate and support the fight-or-flight response. It also provides energy by breaking down fat and increasing blood sugar.
Apart from being responsible for the fight or flight response, adrenaline and noradrenaline are also associated with memory retrieval, attention and vigilance.
When the body cannot produce these important neurotransmitters in sufficient quantities, a person may experience concentration issues, mood changes, and difficulty managing stress.
Tyrosine is also involved in the production of thyroid hormones. The thyroid is a small gland in the neck that is responsible for regulating metabolism, heart rate and blood pressure.
So, diet and/or supplementation?
Early research on tyrosine suggests that it may help counteract the effects of stress by supporting neurotransmitter function, attention, and cognition. A 2015 study supports this claim, suggesting that when stress depletes neurotransmitters, tyrosine supplements may improve cognition.
Tyrosine is sometimes prescribed for mood improvement and to help deal with stress, even to help with cognitive performance. However, excess amounts of tyrosine can lead to an imbalance of thyroid hormones leading to hyperthyroidism.
High protein foods tend to be high in amino acids. So a diet containing whole foods rich in phenylalanine usually means that a person can meet their daily tyrosine needs.
Some foods that are rich in phenylalanine, include:
- soy products, such as soybeans, tofu, and soy milk
- fish and meat, including chicken, turkey, and pork
- eggs and dairy products, such as milk and cheese
- seeds, including pumpkin and sesame seeds
- beans, such as lima beans
Vegetarians and vegans may need to focus on eating more high protein foods, such as tofu, to ensure that they produce enough tyrosine and other amino acids.
Always see your preferred health professional rather than self-prescribing with Tyrosine supplements.
Till the next post,
Live clean n Prosper
(Sources – National Library of Medicine – Science direct -)