Today’s post is about Toxic build-up and the human body.
First, what is a toxin?
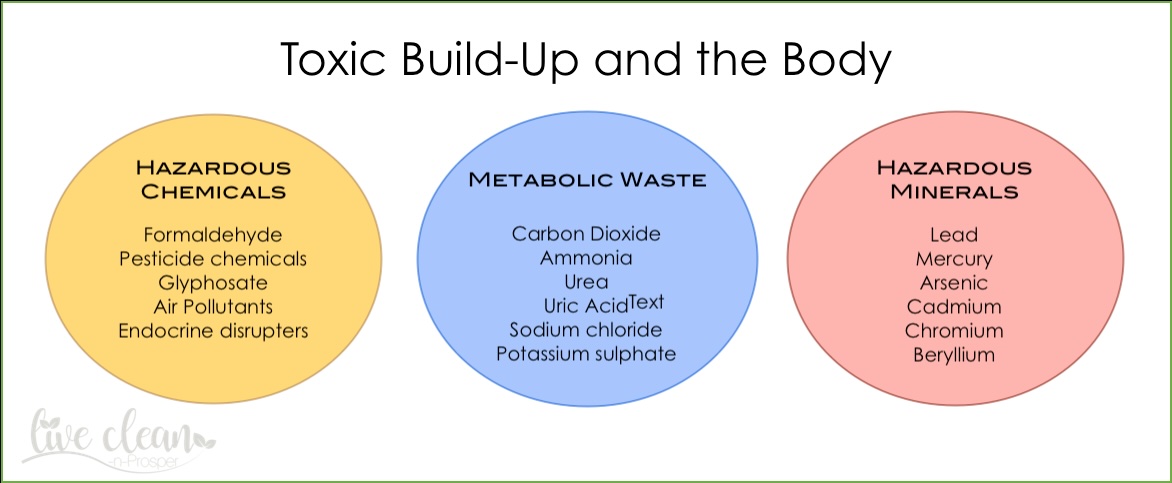
Scientists and doctors don’t have a clear definition of a toxin. They can be the waste products that our body naturally produces, like carbon dioxide. They can also be environmental contaminants which include physical, chemical and biological pollutants and organisms.
We are surrounded by thousands of industrial chemicals. They are in our air, food, water and household products. They come from pesticides, herbicides, smoke, flame retardants (chemicals that make things resistant to fire), and other chemicals used in factories.
We are exposed to these chemicals or toxins on a daily basis. They are in cleaning products, processed, non-organic foods, and food additives. There are also chemicals in personal care products and cosmetics, common kitchen items such as plastic food wraps, containers and non-stick surfaces.
Many of these chemicals have been tested for safety. However, not much is known about the long-term health effects. We know even less about mixtures of these chemicals. What is known is that some of them, like persistent organic pollutants (POPs), have been connected with heart disease, cancer, hormonal problems, growth problems for children, and brain problems.
Is it real or just hype?
It is real. Scientists at the U.S. Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) sampled a number of people living in the United States. Their research revealed that every person in the United States has small amounts of chemicals in their bodies. They even found 200 industrial chemicals, pollutants, and pesticides in newborns. These were absorbed during pregnancy and then via breast milk.
This is what many health practitioners, nutritionists and dietitian’s call ‘toxic build-up’.
This build-up can interfere with our body’s ability to heal itself, therefore compromising the immune system.
How do we get rid of toxins?
Our body has built-in ways to remove toxins. For example, our body produces carbon dioxide when it converts food to energy. Carbon dioxide is a waste product or toxin, and we get rid of it by breathing it out. Other organs that help remove toxins include the liver, skin, kidneys, intestines, lymph nodes, and blood vessels. In addition to breathing out, we remove toxic products through urine, feces, and sweating.
What about a ‘detox’?
Historically people used fasts, saunas, leaches, and practiced bloodletting to ‘purify’ or ‘detox’ their body. There have been only a small number of studies on “detoxification” programs in people. While some have had positive results on weight and fat loss, insulin resistance, and blood pressure, the studies themselves have been of low quality.
There have been no studies on long-term effects of “detoxification” programs.
However, there are ways to reduce our exposure. Studies have shown that when changes are made to diet and lifestyle, reducing the absorption of toxins, the body can more effectively remove them. This is a way of ‘detoxing’.
Reducing intake of processed foods and alcohol, eating fresh, organic produce. Use natural cleaning products. Consider the ingredients in the products you put on our skin, because much of what goes ON you ends up going IN you.
We also did a bit of our own research and found that in Australia there are several different regulatory standards, depending on how the product is classified.
The one common standard in Australia, the US and the EU that we could find is ‘skincare and cosmetics must have a list of ingredients on the label, regardless of whether it is toxic or not.’
So, take the time to read labels and make yourself familiar with the most common nasties. By buying smarter, you can reduce the toxin load on your body, helping it to work better and keeping you in better health.
Till the next post,
Live Clean and Prosper
Sources – U.S. Center for Disease Control and Prevention – National Library of Medicine – University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health