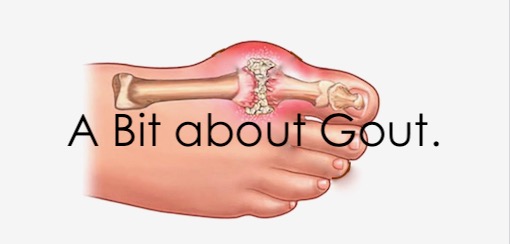
Todays post is about Gout.
Scott and I were recently discussing this condition that affects many people. There are many theories around what it is and how it is contracted.
So, here are some facts.
Gout was historically known as “the disease of kings” or “rich man’s disease”. It has been recognised at least since the time of the ancient Egyptians.
Gout affects about 1 to 2% of the Western population at some point in their lives. It has become more common in recent decades. This is believed to be due to increasing risk factors in the population, such as metabolic syndrome, longer life expectancy, and changes in diet
What is Gout?
Gout is actually a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by crystals that form in and around the joints. The crystals result from high levels of urate in the body. It is a condition caused by a build-up of uric acid and the body does not flush out the crystals fast enough. This build-up usually affects your feet. If you have gout, you’ll probably feel swelling and pain in the joints of your foot, particularly your big toe. Sudden and intense pain, or gout attacks, can make it feel like your foot is on fire.
What is Urate?
Urate is found in all people, in small amounts in our blood. Our bodies make it every day by breaking down natural substances called purines. Purines are found in our bodies’ cells, as well as some of the foods we eat. Our kidneys usually remove any excess urate from our blood into our urine. However, people with gout have higher-than-normal amounts of urate in their bodies. This can be a result of:
- our bodies producing too much urate and/or
- the kidneys being unable to get rid of it quickly enough (this is the main reason for high urate levels in more than nine out of ten people with gout).
If urate levels remain high, it starts to form small crystals in and around the joints. These crystals form slowly, over months or even years, usually without any symptoms. A gout flare up occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the crystals. The crystals still remain in the joint(s) even after the pain settles.
You’re more likely to get gout if you:
*are a middle-aged man or postmenopausal woman
*have parents, siblings, or other family members with gout
*drink alcohol
*take medications such as diuretics and cyclosporine
*if you have a kidney or thyroid problem, or an inherited disorder, can make it harder for your body to remove excess uric acid.
In some people with gout, diet is the cause.
How can diet contribute?
Certain foods are naturally high in purines, which your body breaks down into uric acid. Most people don’t have a problem with high-purine foods. But if your body has trouble releasing excess uric acid, you may want to avoid certain foods and drinks, such as some red and organ meats, certain seafood and alcohol.
Some sugar-sweetened beverages and foods containing fructose can also be problematic, even though they don’t contain purines.
There is however, evidence from studies suggesting that certain foods help can reduce uric acid levels in the body. They are – tart cherries, magnesium, ginger, apple cider vinegar, celery, nettle tea, dandelion and milk thistle seeds.
But simply eating these foods may not be enough to control gout
If left untreated, gout can eventually lead to arthritis. Hard lumps called tophi can eventually develop in your joints and the skin and soft tissue surrounding them. These deposits can permanently damage your joints.
If you think your may be suffering with gout, it is important to seek advise from your chosen health professional.
Moving forward
The only way to diagnose gout with certainty is by your doctor finding urate crystals in fluid taken from your joint. Uric acid levels can also be measured by blood tests, however these are not always accurate. However, blood tests are useful in ruling out other causes for your symptoms, such as joint infections or other forms of arthritis.
The treatment plan recommended will depend on the stage and severity of your gout.
I hope you found this information helpful.
Till the next post,
Live clean n Prosper
Sources – Healthline, Arthritis Australia, Wikipedia