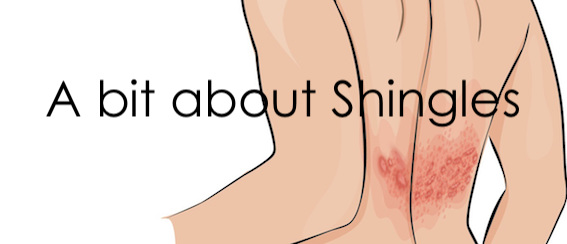
Today’s post is about shingles.
Scott unfortunately contracted this virus recently and he was very uncomfortable with the associated pain.
We decided to do some research on the virus to gain more information about it and determine the best treatment.
As usual, I will share what we learned.
First, what exactly is shingles?
Shingles, also called herpes zoster, is a disease that triggers a painful, blistering skin rash. The same virus as chickenpox, the varicella-zoster virus, causes it. After you recover from chickenpox (usually as a child), the virus continues to live in some of your nerve cells.
For most adults, the virus is inactive and it never leads to shingles. But, for about one in three adults, the virus will become active again and cause the painful condition.
This is because the inactive chickenpox virus stays in the nerve cells near the spine. When the rash develops it’s because the virus has become active again. Usually, a person will only get shingles once in their lives, but it can sometime occur again if you have a weakened immune system.
Why is it so painful?
The intense pain is due to the virus actually damaging the nerves and the nerve fibres in the skin. The pain has been described as a very intense burning sensation creating acute sensitivity of the skin.
After the actual rash goes away, some people may be left with ongoing pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. The pain is felt in the area where the rash occurred.
Living with the PHN pain has been known to cause depression, anxiety, sleeplessness, and weight loss. It can also lead to serious eye problems, including blindness, pneumonia and hearing problems.
The older you are when you get shingles, the greater your chances of developing PHN.
Who is at risk for shingles?
Everyone who has had chickenpox is at risk for developing shingles. Researchers do not fully understand what makes the virus become active again and cause shingles. But some things make it more likely, such as a stressed immune system.
The immune system is the main defence system of the body that responds to infections. Age can affect the immune system. This means that the risk of developing shingles increases as you age. About half of all shingles cases are in adults age 60 or older.
Other factors such as illness, cancer and cancer treatments, too much sun, and organ transplant drugs. Even stress or a cold can weaken your immune system for a short time.
Is it contagious?
If you are in contact with someone who has shingles, you will not get the symptoms of the virus yourself. However, direct contact with fluid from the rash can still spread the varicella-zoster virus. This can cause chickenpox in people who have not had chickenpox before or the chickenpox vaccine. The risk of spreading the virus is low if the shingles rash is kept covered.
How is it treated?
Unfortunately, to date, there is no cure for shingles, but prompt diagnosis and treatment can speed healing and reduce your risk of complications.
There are some options available that may help in conjunction with pharmaceuticals, such as ointments and creams. Researchers have also found that certain essential oils have antiviral and pain-relieving properties. Though further studies are needed, some evidence suggests that these oils, when applied, may help to alleviate pain and itchiness associated with shingles.
These are:
- Neem oil
- St Johns Wort oil
- Peppermint oil
- Capsaicin oil
- Geranium oil
- Thyme oil
- Lemon oil
It seems that the most effective treatment for the herpes zoster virus is prevention and there are vaccinations available to prevent shingles.
Thankfully, due to a fairly quick diagnosis, Scott is recovering well. There is still some continuing PHN, however it is manageable.
We hope you found this information helpful.
Till the next post,
Live clean n Prosper
(Sources – Science Direct– Aust. government Dept. of Health – US National Institute on Ageing – US National Library of Medicine )